| Basic gene Info. | Gene symbol | PRLR |
| Gene name | prolactin receptor |
| Synonyms | HPRL|MFAB|hPRLrI |
| Cytomap | UCSC genome browser: 5p13.2 |
| Type of gene | protein-coding |
| RefGenes | NM_000949.6,
NM_001204314.2,NM_001204315.1,NM_001204316.1,NM_001204317.1,
NM_001204318.1,NR_037910.1, |
| Description | hPRL receptorsecreted prolactin binding protein |
| Modification date | 20141207 |
| dbXrefs | MIM : 176761 |
| HGNC : HGNC |
| Ensembl : ENSG00000113494 |
| HPRD : 01457 |
| Vega : OTTHUMG00000090789 |
| Protein | UniProt: P16471
go to UniProt's Cross Reference DB Table |
| Expression | CleanEX: HS_PRLR |
| BioGPS: 5618 |
| Pathway | NCI Pathway Interaction Database: PRLR |
| KEGG: PRLR |
| REACTOME: PRLR |
| Pathway Commons: PRLR |
| Context | iHOP: PRLR |
| ligand binding site mutation search in PubMed: PRLR |
| UCL Cancer Institute: PRLR |
| Assigned class in mutLBSgeneDB | A: This gene has a literature evidence and it belongs to targetable_mutLBSgenes. |
| References showing study about ligand binding site mutation for PRLR. | 1. "Zhang C, Cherifi I, Nygaard M, Haxholm GW, Bogorad RL, Bernadet M, England P, Broutin I, Kragelund BB, Guidotti JE, Goffin V. Residue 146 regulates prolactin receptor folding, basal activity and ligand-responsiveness: potential implications in breast tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Feb 5;401:173-88. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.12.006. Epub 2014 Dec 15." 25524456
|
| cf) Cancer type abbreviation. BLCA: Bladder urothelial carcinoma, BRCA: Breast invasive carcinoma, CESC: Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, COAD: Colon adenocarcinoma, GBM: Glioblastoma multiforme, LGG: Brain lower grade glioma, HNSC: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, KICH: Kidney chromophobe, KIRC: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, KIRP: Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma, LAML: Acute myeloid leukemia, LUAD: Lung adenocarcinoma, LUSC: Lung squamous cell carcinoma, OV: Ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma, PAAD: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, PRAD: Prostate adenocarcinoma, SKCM: Skin cutaneous melanoma, STAD: Stomach adenocarcinoma, THCA: Thyroid carcinoma, UCEC: Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. |
| LBS | AA sequence | # species | Species |
C36 | PEIHKCRSPDK | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | C36 | PEIFKCRSPNK | 1 | Homo sapiens | C36 | PTIIKCRSPEK | 1 | Gallus gallus | C36 | PKLVKCRSPGK | 1 | Bos taurus | D211 | TRCKPD-HGYW | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | D211 | VRCKPD-HGYW | 1 | Homo sapiens | D211 | IHCKPDHHGSW | 1 | Gallus gallus | D211 | IRCKPD-HGYW | 1 | Bos taurus | H212 | CKPD-HGYWSR | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | H212 | CKPD-HGYWSA | 1 | Homo sapiens | H212 | CKPDHHGSWSE | 1 | Gallus gallus | H212 | CKPD-HGYWSE | 1 | Bos taurus | H65 | YSLTYSKEGEK | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | H65 | YSLTYHREGET | 1 | Homo sapiens | H65 | YTLLYSKEGEE | 1 | Gallus gallus | H65 | YTLTYHKEGET | 1 | Bos taurus | I100 | IWKIYIITVNA | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | I100 | MWRTYIMMVNA | 1 | Homo sapiens | I100 | FWTIYNITVRA | 1 | Gallus gallus | I100 | IWKMYVITVNA | 1 | Bos taurus | K35 | KPEIHKCRSPD | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | K35 | KPEIFKCRSPN | 1 | Homo sapiens | K35 | KPTIIKCRSPE | 1 | Gallus gallus | K35 | KPKLVKCRSPG | 1 | Bos taurus | M102 | KIYIITVNATN | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | M102 | RTYIMMVNATN | 1 | Homo sapiens | M102 | TIYNITVRATN | 1 | Gallus gallus | M102 | KMYVITVNAIN | 1 | Bos taurus | R37 | EIHKCRSPDKE | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | R37 | EIFKCRSPNKE | 1 | Homo sapiens | R37 | TIIKCRSPEKE | 1 | Gallus gallus | R37 | KLVKCRSPGKE | 1 | Bos taurus | T63 | TNYSLTYSKEG | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | T63 | TNYSLTYHREG | 1 | Homo sapiens | T63 | TNYTLLYSKEG | 1 | Gallus gallus | T63 | TNYTLTYHKEG | 1 | Bos taurus | W215 | D-HGYWSAWSP | 1 | Homo sapiens | W215 | DHHGSWSEWSS | 1 | Gallus gallus | W215 | D-HGYWSRWGQ | 1 | Mus musculus | W215 | D-HGYWSRWSQ | 1 | Rattus norvegicus | W215 | D-HGYWSEWSP | 1 | Bos taurus | W47 | ETFTCWWRPGT | 1 | Homo sapiens | W47 | ETFTCWWKPGL | 1 | Gallus gallus | W47 | ETFTCWWNPGS | 1 | Mus musculus | W47 | ETFTCWWNPGT | 1 | Rattus norvegicus | W47 | ETFTCWWEPGA | 1 | Bos taurus | Y214 | PD-HGYWSAWS | 1 | Homo sapiens | Y214 | PDHHGSWSEWS | 1 | Gallus gallus | Y214 | PD-HGYWSRWG | 1 | Mus musculus | Y214 | PD-HGYWSRWS | 1 | Rattus norvegicus | Y214 | PD-HGYWSEWS | 1 | Bos taurus | Y64 | NYSLTYSKEGE | 2 | Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus | Y64 | NYSLTYHREGE | 1 | Homo sapiens | Y64 | NYTLLYSKEGE | 1 | Gallus gallus | Y64 | NYTLTYHKEGE | 1 | Bos taurus |
 Gene summary
Gene summary  Gene ontology having evidence of Inferred from Direct Assay (IDA) from Entrez
Gene ontology having evidence of Inferred from Direct Assay (IDA) from Entrez  Lollipop-style diagram of mutations at LBS in amino-acid sequence.
Lollipop-style diagram of mutations at LBS in amino-acid sequence. 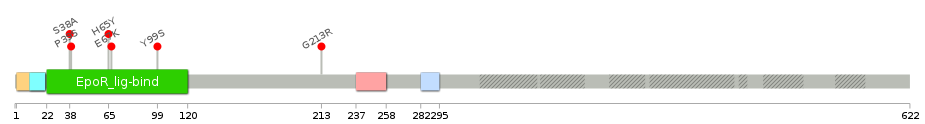
 Cancer type specific mutLBS sorted by frequency
Cancer type specific mutLBS sorted by frequency Relative protein structure stability change (ΔΔE) using Mupro 1.1
Relative protein structure stability change (ΔΔE) using Mupro 1.1  : nsSNV at non-LBS
: nsSNV at non-LBS : nsSNV at LBS
: nsSNV at LBS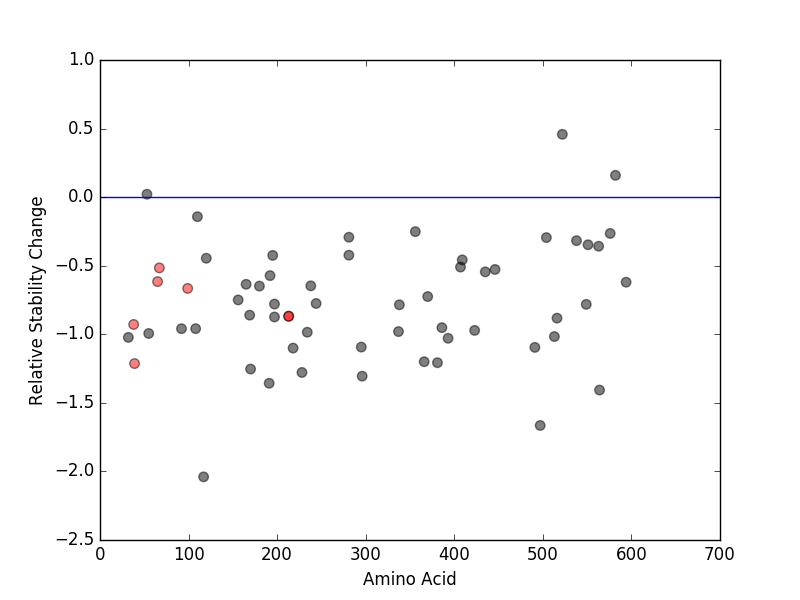
 nsSNVs sorted by the relative stability change of protein structure by each mutation
nsSNVs sorted by the relative stability change of protein structure by each mutation  Structure image for PRLR from PDB
Structure image for PRLR from PDB Differential gene expression between mutated and non-mutated LBS samples in all 16 major cancer types
Differential gene expression between mutated and non-mutated LBS samples in all 16 major cancer types Differential co-expressed gene network based on protein-protein interaction data (CePIN)
Differential co-expressed gene network based on protein-protein interaction data (CePIN) Gene level disease information (DisGeNet)
Gene level disease information (DisGeNet)  Mutation level pathogenic information (ClinVar annotation)
Mutation level pathogenic information (ClinVar annotation)  Gene expression profile of anticancer drug treated cell-lines (CCLE)
Gene expression profile of anticancer drug treated cell-lines (CCLE)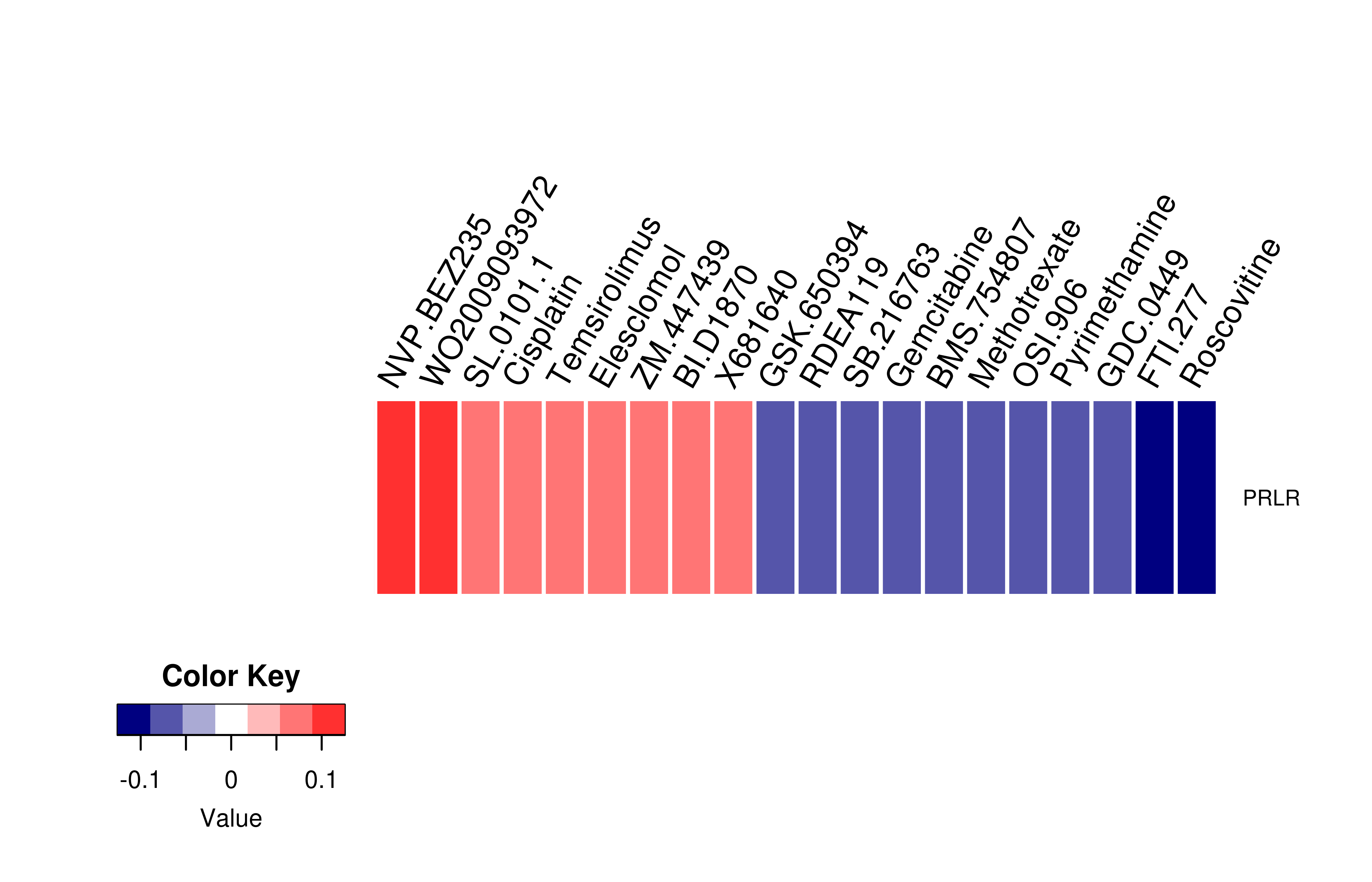
 Gene-centered drug-gene interaction network
Gene-centered drug-gene interaction network 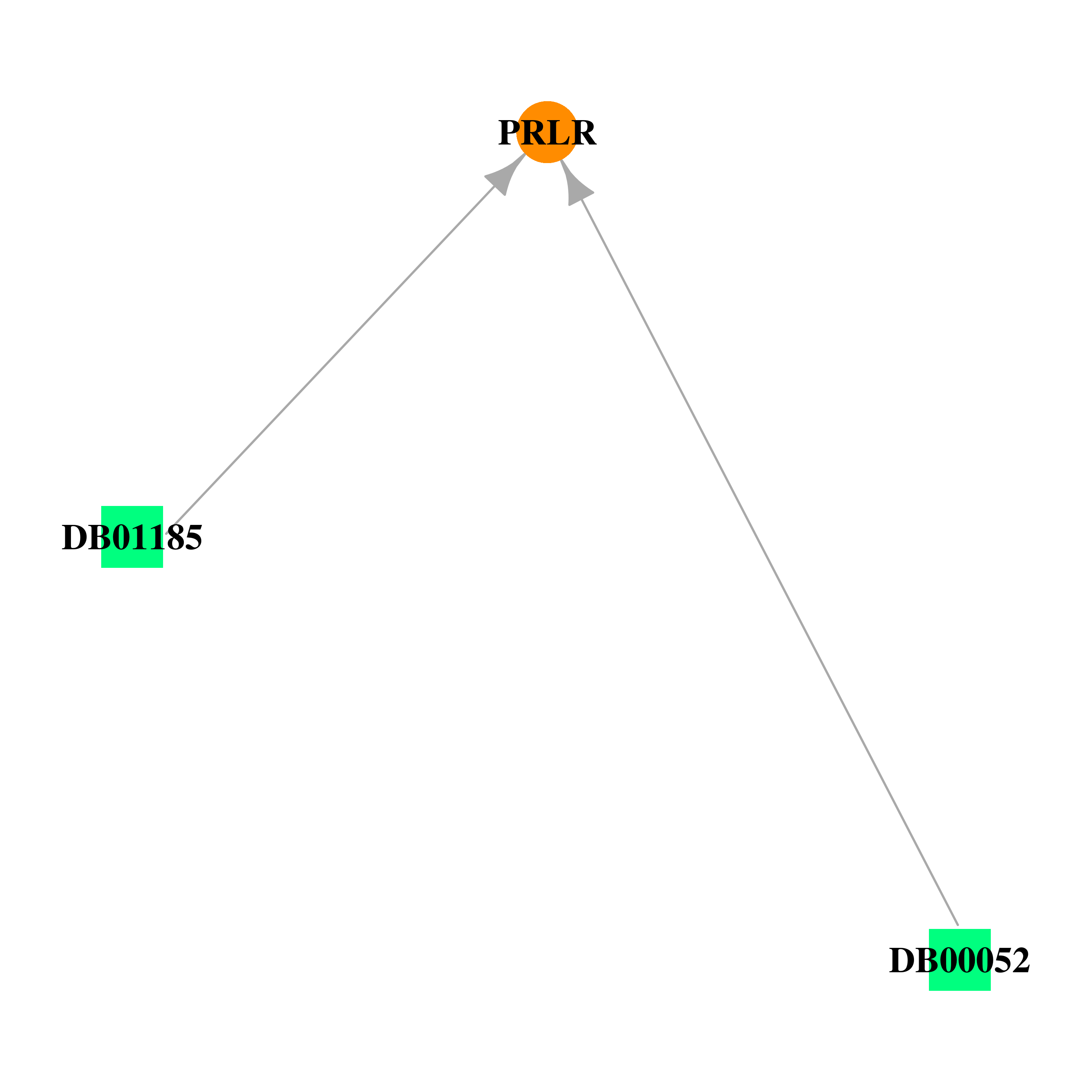
 Drug information targeting mutLBSgene (Approved drugs only)
Drug information targeting mutLBSgene (Approved drugs only)

 Gene-centered ligand-gene interaction network
Gene-centered ligand-gene interaction network 
 Ligands binding to mutated ligand binding site of PRLR go to BioLip
Ligands binding to mutated ligand binding site of PRLR go to BioLip Multiple alignments for P16471 in multiple species
Multiple alignments for P16471 in multiple species 
